Notes of CSAPP--Memory
本文总结了CSAPP一书中和memory相关的内容
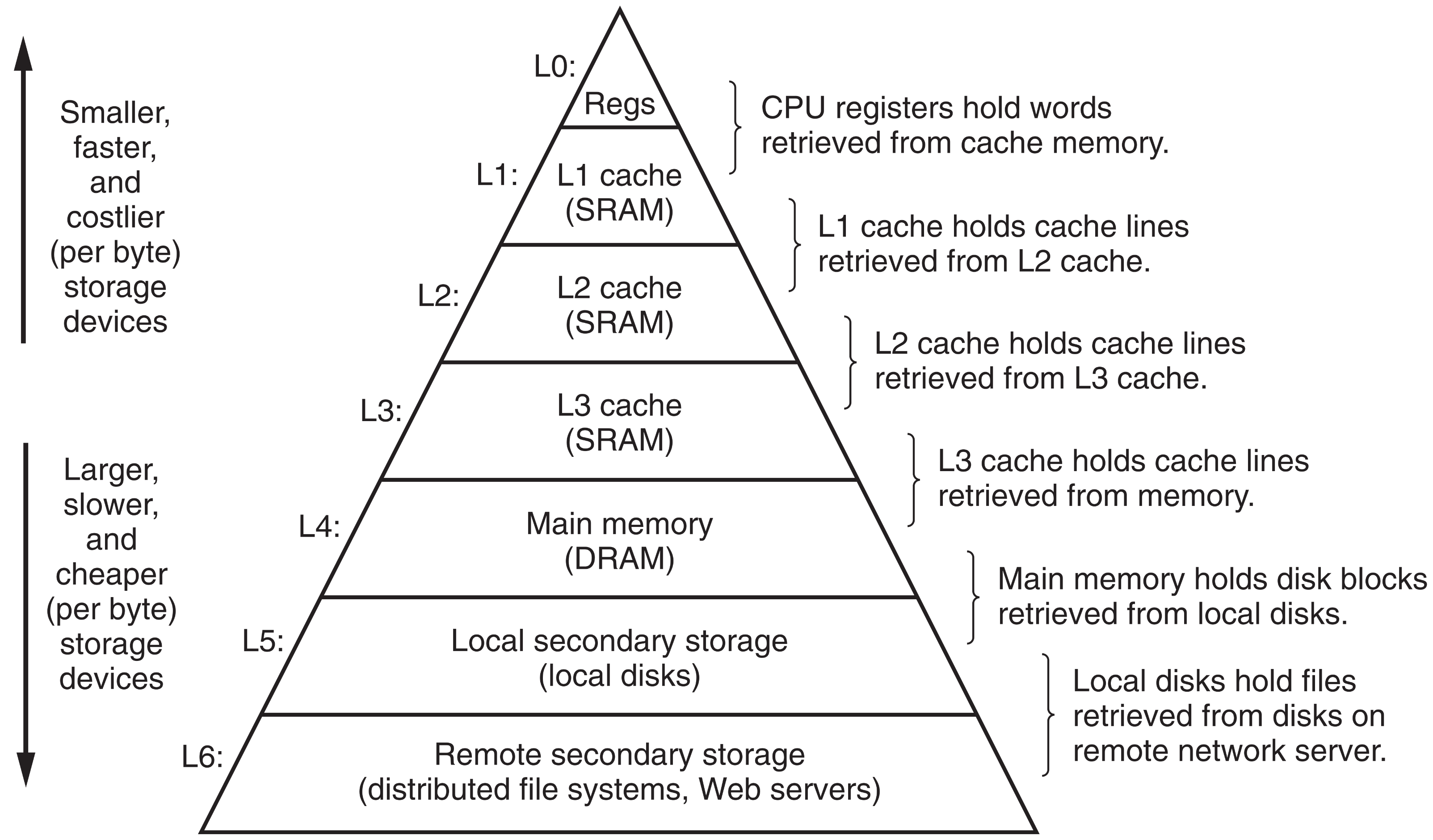
上图描述了现代计算机的存储体系,从L0开始到L6,其中L0就是CPU寄存器,L2和L3两级缓存[Cache],它们直接建构在CPU Die上,L4就是我们常说的计算机内存,L5是直接通过PCIe链接的本机硬盘,而最后L6则是通过网络连接的网络硬盘。
Locality and CPU-Cache-DRAM hierarchy/boundary
This idea centers around a fundamental property of computer programs known as locality. Programs with good locality tend to access the same set of data items over and over again, or they tend to access sets of nearby data items. Programs with good locality tend to access more data items from the upper levels of the memory hierarchy than programs with poor locality, and thus run faster.
Locality,一般翻译为局部性,是非常重要的计算机系统概念,指计算机程序会倾向于访问最近的数据,或者是访问与上次访问数据距离近的数据。
CPU-Cache-DRAM hierarchy,当数据在这三个层级移动时,如果CPU无法直接在Register中访问到计算需要的数据,就会访问Cache,如果Cache里也没有,就会访问Memory,此时,如果获得数据,则会将数据放到Cache中[具体放在哪一级或者哪几级的Cache,不同的CPU使用不同的策略],然后在放到Register中。但对于L5或者L6中,则无此机制,L6获得的数据不一定要存储在L5即本地硬盘中,可以直接放到L4中。
一般情况下:Cache访问速度是Memory的10-30倍,memory的访问速度是SSD的100倍,而SSD的访问速度一般是HDD的100倍,所以,如果能在CPU-Cache-DRAM hierarchy中访问到数据,就尽量不要访问到硬盘。
Vritual Memory
虚拟内存可能是现在计算系统最重要的概念,其主要实现方式是在disk上开辟出一块空间,其大小一般情况下和内存大小一致,称为swap space,我们每次安装操作系统的时候可能都会被要求设置swap space的大小,就是用来干这个的。
这样在memory满了的时候,可以将暂时用不上的page,先放到swap space而不影响程序运行。本质上说swap space充当了memory的overflow space,而如何对page在memory和vritual memory之间调度,不同的操作系统有不同的机制。
Reference:
- Computer Systems: A Programmer’s Perspective[(3rd Ed)], Section 1.6
- Computer Systems: A Programmer’s Perspective[(3rd Ed)], Section 1.7.3
- Computer Systems: A Programmer’s Perspective[(3rd Ed)], Section 6
- Computer Systems: A Programmer’s Perspective[(3rd Ed)], Section 9